Published
4 years agoon

The first week-and-a-half after a COVID-19 patient is released from the hospital can be especially dangerous.
That’s the takeaway from a new study published by JAMA conducted by a team from the University of Michigan and the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System.
The researchers compared post-hospital outcomes for nearly 2,200 veterans who survived their coronavirus hospitalizations at 132 VA hospitals last spring and early summer.
The study included outcomes from the Fresno VA Medical Center,
“There seemed to be this very vulnerable period in the first 10 to maybe 14 days after hospital discharge,” Dr. Hallie Prescott, one of the study’s authors, told GV Wire℠ by Zoom.
Rates of readmission or death were higher than for pneumonia or heart failure during the first 10 days after discharge following COVID-19 hospitalization.
In the first two months, 9% of the COVID-19 patients who survived hospitalization had died, and almost 20% had suffered a setback that sent them back to the hospital.
That’s on top of the 18.5% who died during hospitalization.

“There seemed to be this very vulnerable period in the first 10 to maybe 14 days after hospital discharge.” – Dr. Hallie Prescott, one of the study’s authors
“When we looked at why they came back to the hospital, by far the most common reasons were COVID, pneumonia, and sepsis,” said Prescott. “So it really seemed to be that patients were experiencing this kind of delayed worsening of their symptoms that then brought them back to their hospital.”
The most common reasons listed for rehospitalization were COVID-19, cited in 30% of patients, and sepsis seen in 8.5%. More than 22% of the readmitted veterans went to an intensive care unit.
The authors studied Veterans Affairs hospitals data because it was readily available and represented a wide swath of the country.
“It’s a huge system with patients across the entire country, whereas, other studies have been done looking at maybe single hospitals or even like a single group of hospitals,” said Prescott.
She says other large data sets like Medicare or state discharge databases generally have a long lag time.

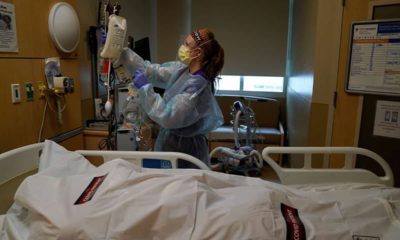
U.S. Air Force Capt. Raquel Dixon, registered nurse, 60th Medical Group, provides patient care at Community Regional Medical Center in Fresno, on Aug. 4, 2020. A new study indicates that the first 10 days after release from a hospital pose high risks for COVID-19 patients. (MI Army National Guard photo by Spc. Aaron Good)
The study didn’t include non-veterans treated at VA hospitals.
All but 5% of the patients were male, and half were Black, which is not nationally representative but focuses on two high-risk groups. But within the veterans studied, the only factor that made a significant difference in outcomes was age; about half of veterans in their 70s and 80s died in the 60 days after leaving the hospital.
Prescott is interested in learning more about patient vulnerability right after leaving a hospital, and not just for COVID-19.
“Trying to understand what different hospitals or systems are doing to try to help support patients during those first weeks to try to learn what seems to be successful and what might be kind of shareable to other hospitals and systems across the country,” Prescott said. “(That’s) the question that I’m currently more interested in.”
She also says some of the outcomes may improve as better therapies and techniques are utilized by hospitals.
The hope is to continue to study new data from VA and non-VA hospitals as it becomes available.
Prescott is also the senior author of another recent paper showing slow recovery in COVID-19 patients hospitalized in Michigan hospitals during the state’s spring surge. That study showed nearly 23% of COVID patients said they became short of breath just climbing a flight of stairs. One-third had ongoing COVID-like symptoms, including many who still had problems with taste or smell.
Of those who had jobs before their bout with COVID-19, 40% said they couldn’t return to work; most because of their health and some because they’d lost their job. And 26% of those who resumed work said their health forced a cutback in duties or hours.
Nearly half of those interviewed said they’d been emotionally affected by their experience with COVID-19. Some sought mental health treatment.


Bay Area Restaurants, Wineries File Lawsuit Over Outdoor Dining Ban


Madera Hospital, With ICU Inundated, Transfers Patients to Other Facilities

‘Shameful’: US Virus Deaths Top 400k as Trump Leaves Office


Bill McEwen: Five Steps to Heal America Under Biden


Trustee Slatic Calls for ‘Redshirt’ Year for High Schoolers When In-Person Classes Resume
Anger in States Over Pace of COVID-19 Vaccine Allotments




